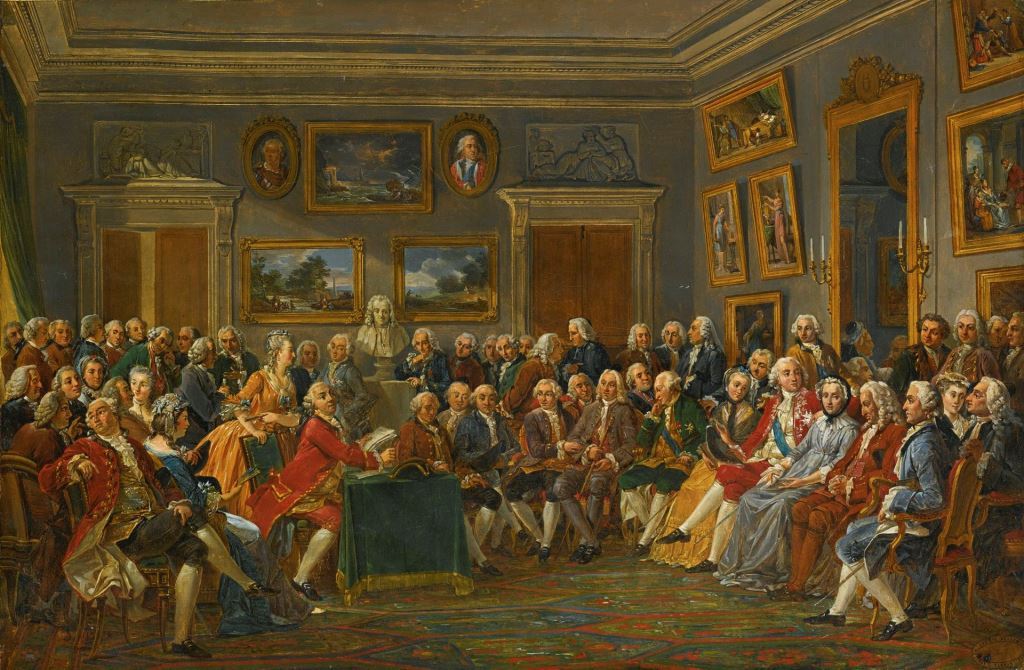
The Enlightenment laid the groundwork for modern society, emphasizing reason and science. Today, we face new global challenges that the original Enlightenment ideals alone cannot fully address. Enlightenment 2.0 seeks to update these principles, integrating diverse perspectives and ethical considerations to navigate the complexities of the 21st century.
Introduction to Enlightenment 2.0
Enlightenment 2.0 and the New Enlightenment refer to the same evolving concept—an effort to revive and modernize the ideals of the original Enlightenment, updating them to address the unique challenges of the 21st century. These terms highlight a shared goal: adapting reason, science, and ethical progress to navigate global problems such as climate change, inequality, and technological disruption.
The Original Enlightenment: Foundation for Modernity
The Enlightenment of the 17th and 18th centuries, often called the “Age of Reason,” championed reason, science, and the pursuit of individual rights. Philosophers like Immanuel Kant, Voltaire, and Adam Smith laid the groundwork for modern democracy and human rights by challenging the authority of monarchies and religious institutions, advocating secular governance, and promoting freedom of thought. However, while transformative, the original Enlightenment emerged from a Western European context and was often limited by its Eurocentric and colonial biases.
The Shape of a New Enlightenment
Enlightenment 2.0 is not a singular, universally defined concept but an evolving idea interpreted in various ways by different thinkers, writers, and scholars. Unlike the original Enlightenment, which often sought clear, universal truths, Enlightenment 2.0 acknowledges the complexity and uncertainty of the modern world. It promotes nuanced and adaptable approaches to solving global problems, integrating digital and technological advancements to enhance human well-being and freedom.
But for this to be more than just an update of the past, a new Enlightenment must go further. It must move beyond abstraction and linear thinking. It must recognise the limits of reductionism and embrace ambiguity, context, and multiple ways of knowing. It should value not just scientific knowledge, but also lived experience, embodied understanding, and indigenous wisdom. It must be more relational than rationalist, more humble than heroic.
A new Enlightenment would bring ethics, aesthetics, and narrative back into the centre of our collective efforts. It would foster distributed, collaborative sensemaking rather than top-down control. It would prioritise practical wisdom, adaptability, and creativity over certainty and uniformity. This is not about rejecting the old Enlightenment, but about building on its legacy in a way that makes space for the complexity of our time.
Some, such as Dave Snowden, have suggested that “Enlightenment” may not be the right word at all. What we need now is less a new Enlightenment and more a new Renaissance—a rebirth of imagination, art, and cross-disciplinary creativity. A rediscovery of how science and story, data and myth, structure and spontaneity, can live together in creative tension. A space for reimagining, not just reasoning.
I understand that suggestion, but I’m still comfortable using the term New Enlightenment. Not because I want to return to the old one, but because the word new does its work. It signals that we are not continuing the same project, but transforming it. It’s familiar enough to be a bridge—and open enough, I hope, to carry something genuinely different.
Global and Ethical Dimensions of the New Enlightenment
One of the key tenets of Enlightenment 2.0 is its emphasis on global perspectives and inclusivity. It critically examines the Eurocentric nature of the original Enlightenment and seeks to incorporate diverse intellectual traditions from around the world. This is crucial for addressing global challenges like climate change, pandemics, and social inequality, which require collective, international solutions.
The New Enlightenment also focuses on reevaluating human progress. Instead of measuring success solely by economic growth, it calls for new metrics that prioritize sustainability, well-being, and equity. This cultural shift away from consumerism and materialism echoes the growing recognition that human progress must be aligned with the preservation of the planet’s resources and the promotion of social justice.
Sustainability and Ethical Imperatives
At the core of the New Enlightenment is a focus on sustainability and ecological balance. Thinkers like Marcelo Gleiser, for example, advocate for “Humancentrism,” a concept that places the preservation of life on Earth at the heart of human progress. This approach reflects the growing urgency to address environmental degradation, as unchecked consumption and technological advancement have pushed the planet to its limits.
Enlightenment 2.0 promotes a cultural and moral shift towards living more sustainably. It calls for rethinking our relationship with nature and developing ethical systems that protect both human and non-human life. This marks a departure from the original Enlightenment’s more anthropocentric focus, emphasizing that progress must now include the well-being of the planet as an essential component.
Key Initiatives
A significant initiative within this framework is the European Commission Joint Research Council’s (JRC) multi-year research program, also named “Enlightenment 2.0,” which began in 2018. This initiative seeks to understand the various drivers influencing political decision-making in the 21st century.
As part of this effort, the JRC has published several key reports, including:
- Understanding Our Political Nature (2019)
- Technology and Democracy (2020)
- Values and Identities (2021)
These reports explore the complex interplay of values, identities, and technological factors that shape contemporary political landscapes, aiming to inform and improve policymaking in an increasingly complex world.
Core Principles of Enlightenment 2.0
At its core, Enlightenment 2.0 advocates for a renewed commitment to rationalism and scientific inquiry, particularly in an era of rising misinformation, pseudoscience, and anti-intellectualism. It also underscores the importance of ethical and moral progress, stressing that technological and scientific advances must be guided by strong ethical principles, especially regarding pressing issues like climate change, inequality, and human rights.
Tag: enlightenment (1)
Tag: Enlightenment 2.0 (12)
Global Perspective
Enlightenment 2.0 adopts a global perspective, recognizing that the original Enlightenment was primarily a Western European movement. This modern version seeks to incorporate diverse perspectives and knowledge systems from around the world, understanding that global challenges require global solutions. Enlightenment 2.0 also calls for a critical examination of the original Enlightenment’s limitations and failures, particularly its connections to colonialism, Eurocentrism, and the exploitation of nature.
Entanglement and Enlightenment
In exploring Enlightenment 2.0, we must also consider the complexity of today’s interconnected systems, a theme closely tied to the concept of entanglement. As explored in the work of Dave Snowden and Danny Hillis, modern society is deeply intertwined with technology, creating unpredictable outcomes that traditional Enlightenment thinking cannot fully address. Enlightenment 2.0 acknowledges this complexity by integrating diverse perspectives and promoting adaptive, holistic approaches. The Age of Entanglement emphasizes the need for synthesis, where progress is achieved not by breaking things down but by understanding and navigating the interconnectedness of our systems.
Notable Contributions
 In addition to the JRC’s program, other notable contributions to the Enlightenment 2.0 discourse include:
In addition to the JRC’s program, other notable contributions to the Enlightenment 2.0 discourse include:- Joseph Heath’s book “Enlightenment 2.0”, published in 2014, outlines a program for a second Enlightenment.
- The Royal Society of Arts (RSA) ran a project called “21st-Century Enlightenment,” with a report published in 2010, emphasizing the need to rethink and reinvigorate Enlightenment ideals in the context of contemporary challenges.
A New Enlightenment | Steven Pinker (source)
The New Enlightenment and the Fight to Free Knowledge | Peter B. Kaufman (source)
Tag: Enlightenment 2.0 (12)


Overall, Enlightenment 2.0 is about reimagining the core values of the original Enlightenment—reason, science, human rights, and progress—to better address the complex challenges of our current era. It serves as a critique of and a continuation of Enlightenment ideals adapted for today’s world.
To tackle the challenges of the 21st century, it is essential to adopt the principles of Enlightenment 2.0. This involves a strong commitment to rational thought, ethical progress, and inclusivity. By revisiting and applying these values while advancing human rights and scientific knowledge, we can address global issues more effectively.
Resources
- Podcast: Welcome to the Second Enlightenment by James Lindsay
Posts that link to this post
- From Enlightenment to Entanglement Adapting to the complexities of an interconnected world
POST NAVIGATION
CHAPTER NAVIGATION
SEARCH
Blook SearchGoogle Web Search
Photo Credits: MidJourney (Public Domain)
This coaching supports you in leading as a practice: initiating conversations that matter, deepening connection, and making space for reflection where it's often missing.