Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts or tendencies that our brain uses to process information and make judgments. They can lead us to make poor decisions, overlook important details, and draw incorrect conclusions.
Introduction
Cognitive biases are mental shortcuts or tendencies that our brain uses to process information and make judgments. These biases can affect our reasoning and decision-making skills and lead us to make judgments that are not based on objective reality.
Some common cognitive biases include confirmation bias, where we tend to seek out and pay more attention to information that supports our existing beliefs and ignore information that contradicts them; the sunk cost bias, where we are more likely to continue investing time, money, or effort into something because we have already invested a lot in it, even if it is not rational to do so; and the framing effect, where our decision-making is influenced by how information is presented to us.
Other examples of cognitive biases include the availability heuristic, the anchoring bias, and the halo effect. You can find more information about these and other cognitive biases on Wikipedia or by web search. Wikipedia lists over 180 cognitive biases.
Tag: cognitive bias (28)
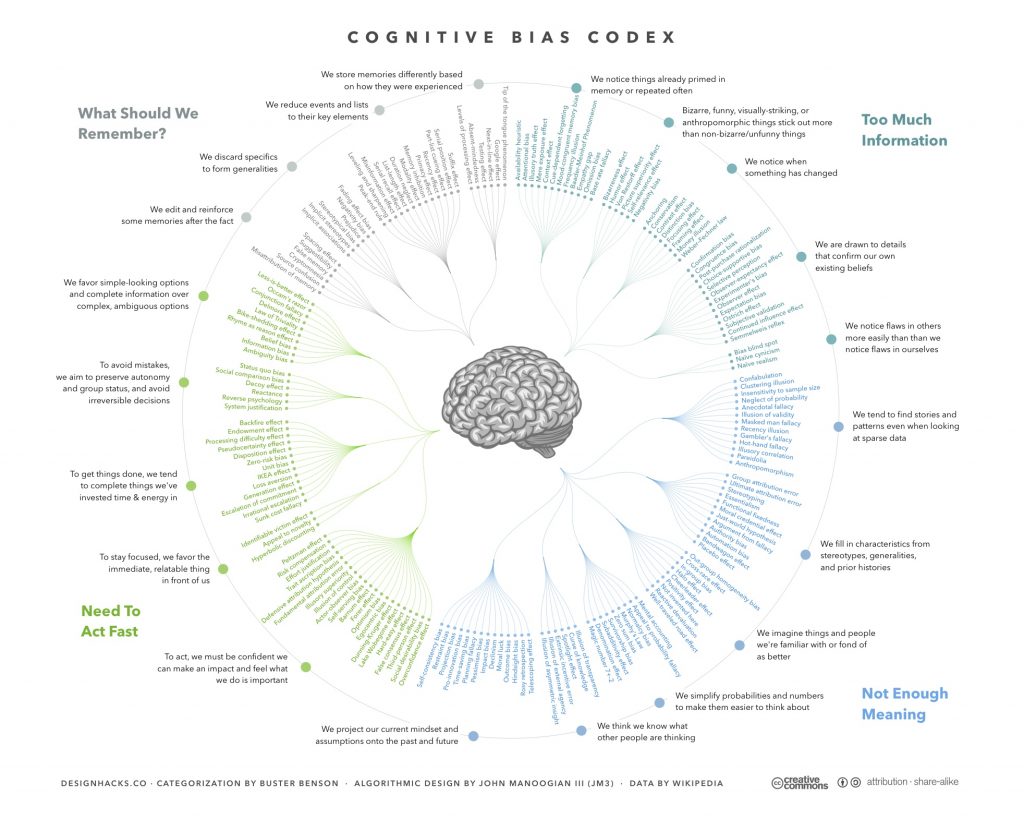
The impact of cognitive biases
The impact of cognitive biases on our reasoning capability can be significant. They can lead us to make poor decisions, overlook important information, and draw incorrect conclusions.
Additionally, cognitive biases can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts in conversation with others, as we may interpret their words and actions differently due to our biases.
The evolution of cognitive biases
From an evolutionary perspective, cognitive biases are a strange phenomenon.
Our reasoning ability is riddled with so many cognitive biases that our ability as individuals to make sound sense of the world is severely impacted.
It seems strange that evolution would have done a sloppy job on one of the human mind’s crucial capabilities.
Unless, of course, these seeming design flaws were not flaws at all but features.
Resources
- Wikipedia: Cognitive bias
- Wiley Onlne Library: The Evolution of Cognitive Bias
Detailed Resources
- Article: Embodied Cognition by Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (2021)
Posts that link to this post
- The Allure of Simple Stories We tend to readily accept uncomplicated narratives without verification
- The Fallibility of Science Understanding the limits and strengths of science
- The Impact of Cognitive Biases in Conversation Cognitive biases can lead to flawed or irrational conclusions in a conversation
- The Scientific Method The backbone of modern science
POST NAVIGATION
CHAPTER NAVIGATION
SEARCH
Blook SearchGoogle Web Search
Photo Credits: Gerd Altmann (CC0 1.0) | Wikimedia Commons (CC BY-SA 4.0)
The Gurteen Knowledge Letter is a free monthly newsletter with over 20,000 subscribers that I have been publishing by email for over 20 years.
Learn more about the newsletter and register here.