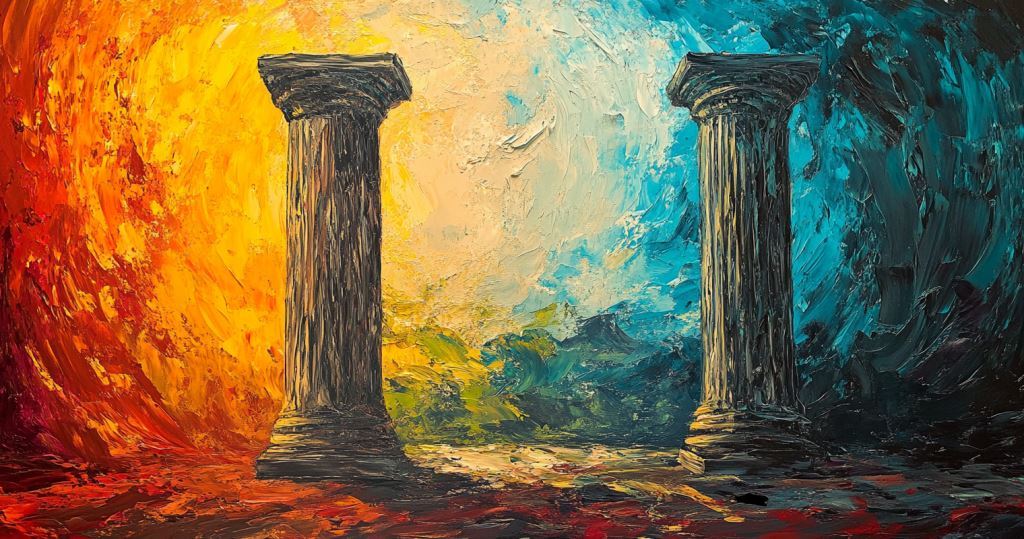
Introduction: Two Pillars of Truth The convergence of science and philosophy in the pursuit of knowledge
In this chapter, I explore the two foundational pillars of truth-seeking: the scientific method and the Socratic elenchus. The pursuit of truth is not just an intellectual exercise; it is a necessity in an age where science and technology drive much of our existence. In a powerful interview, Carl Sagan warned of the dangers of a society that relies heavily on science and technology yet remains … Continue reading Introduction: Two Pillars of Truth The convergence of science and philosophy in the pursuit of knowledge